Buscar este blog
Mostrando entradas con la etiqueta permanent immigrants. Mostrar todas las entradas
Mostrando entradas con la etiqueta permanent immigrants. Mostrar todas las entradas
martes, 12 de febrero de 2019
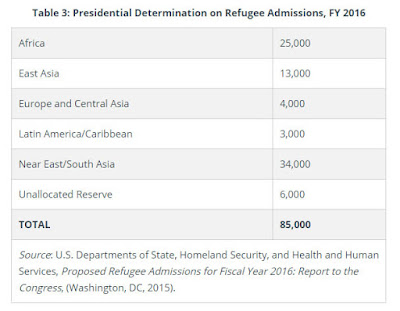
U.S. immigration law is very complex, and there is much confusion as to how it works. The Immigration and Naturalization Act (INA), the body of law governing current immigration policy, provides for an annual worldwide limit of 675,000 permanent immigrants, with certain exceptions for close family members. Lawful permanent residency allows a foreign national to work and live lawfully and permanently in the United States. Lawful permanent residents (LPRs) are eligible to apply for nearly all jobs (i.e., jobs not legitimately restricted to U.S. citizens) and can remain in the country even if they are unemployed. Each year the United States also admits noncitizens on a temporary basis. Annually, Congress and the President determine a separate number for refugee admissions.
In order to be admitted through the family-based immigration system, a U.S. citizen or LPR sponsor must petition for an individual relative, establish the legitimacy of the relationship, meet minimum income requirements, and sign an affidavit of support stating that the sponsor will be financially responsible for the family member(s) upon arrival in the United States.
In FY 2014, immigrants admitted through the employment preferences made up 15 percent of all new LPRs in the United States.
Asylum is available to persons already in the United States who are seeking protection based on the same five protected grounds upon which refugees rely. They may apply at a port of entry at the time they seek admission or within one year of arriving in the United States. There is no limit on the number of individuals who may be granted asylum in a given year nor are there specific categories for determining who may seek asylum. In FY 2014, 23,533 individuals were granted asylum.
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)